Decades of experience in a range of industries
Proven processes for smooth delivery
Engineering and design expertise
Sonic Welding Solutions
When it comes to plastic joining techniques, there are only a few methods that stand up to the demands of industrial manufacturing: adhesive gluing, threaded fastening and ultrasonic welding. Adhesive bonding and bolting are both more mature technologies, whereas sonic welding is the relatively newer joint design that has carved out a niche in fast, low complexity, nonstructural plastic joining projects.
Overall, there is a need for all three joining styles in the industry, each with their ideal applications. Read on to learn more about ultrasonic technology and how it compares to its rival joining techniques.
Building With Sound: The Fundamentals of Sonic Weld Joining
Sonic welding is accomplished by either handheld or automated joining systems that share the same operating principles: Two separate material pieces are placed into a workstation where they are physically pressed together between a welding arm and a solid anvil underneath. The welding arm is made up of a sonic welding converter, booster and sonotrode (or horn), altogether powered by a sonic welding controller.
When the welder is activated, the weld horn receives physical vibrations from the converter and booster set attached above it, which pushes the horn down into the materials below by a certain dimension (the amplitude), and then does so repeatedly up and down, again and again (the frequency). So, a complete sonic weld specification incorporates both factors, reading as in this example: "15 µm amplitude @ 30 kHz frequency." This weld spec means that the weld horn will stroke up and down a length of 15 µm (microns) similar to a miniature jackhammer, and will do so at 30,000 strokes per second.
This is how a sonic weld joint is created; by mechanical vibrations generating enough friction between separate material pieces that the two become fused into one solid object.
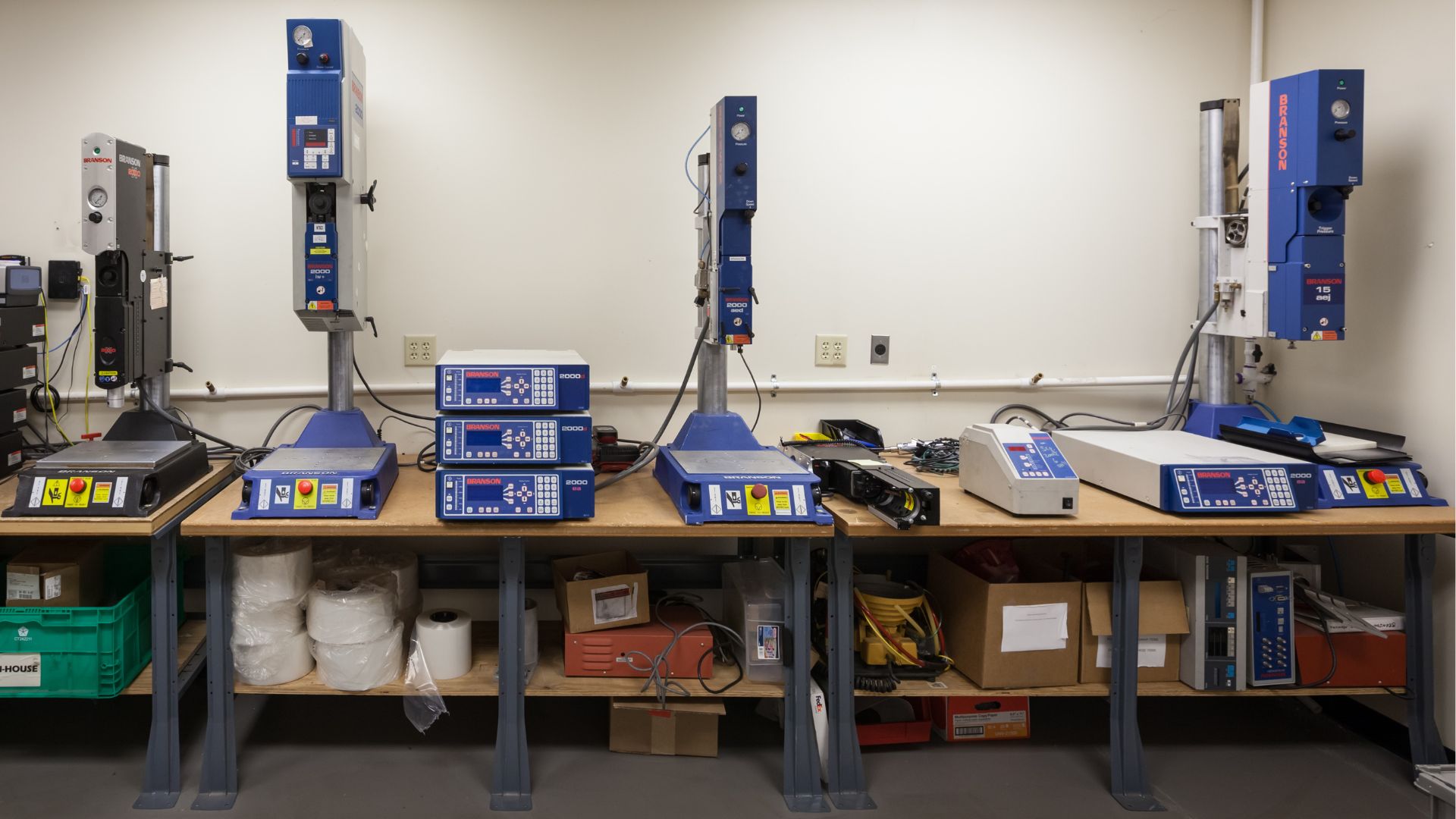

Sonic Welded Joints, Hidden in Plain Sight
Sonic welds are all around us both at work and at home, often in products we encounter every day. Examples include:

MRO (Maintenance, Repair and Operations) Parts
Motor guards, seal kits, retainer clip kits, service tools and all manner of plastic replacement parts.
Information Technology and Computing
Computer chassis, printed circuit boards, expansion cards, wiring cordsets, component housings, networking hardware, laptops and cooling components.

Fabrics and Textiles
Vehicle headliners, upholstery liners, furniture covers, canvas tie-down points, industrial protective sheeting, recreational vehicle covers and clothing accessories.
Designing for Sonic Success: Material Considerations
Automating Sonic Welding Processes
Manual Sonic Welding
Usually performed on a benchtop using a handheld sonotrode. Manual sonic welding can produce one weld at a time and is subject to the skill and consistency of the operator in achieving high-quality welds consistently.
Ultrasonic Joint Testing
Performed using an equipment station in which parts are lined up and situated by a human operator. Once the parts are loaded, actuated sonotrodes are extended to the weld locations, the welds are executed and the completed joined assembly is then removed from the system by hand.
Fully Automated Sonic Welding
The most efficient welding option, can automatically feed in parts to be welded, align and orient the parts in the weld bay, robotically position multiple sonotrodes to the weld points, run quality confirmation checks, execute the welds and then discharge the part to make room for the next part in line. All virtually hands-free.
AMS offers two plastic joining system platforms that can provide sonic welding along with other plastic fabrication processes. They differ in their automation levels.
- Our AMS PJ-301 is a versatile, semi-standard system for ultrasonic staking, forming and spot welding. With semi-automatic operation, poka-yoke functions and outstanding productivity, the PJ-301 is a great general purpose plastic joining machine. This system is easily reconfigurable for future requirements.
- Our AMS PJ-401 is designed for high-volume ultrasonic plastic welding applications requiring precise welding profiles and specifications, exact locations, high levels of error-proofing and repeatability to ensure consistent welding. The PJ-401 offers larger part sizes, higher volumes, shorter cycle times, advanced recipe-driven PLC controls and extensive data reporting.