Decades of experience in a range of industries
Proven processes for smooth delivery
Engineering and design expertise
Spin Welding's Role in Industrial Manufacturing
The Spin Welding Process
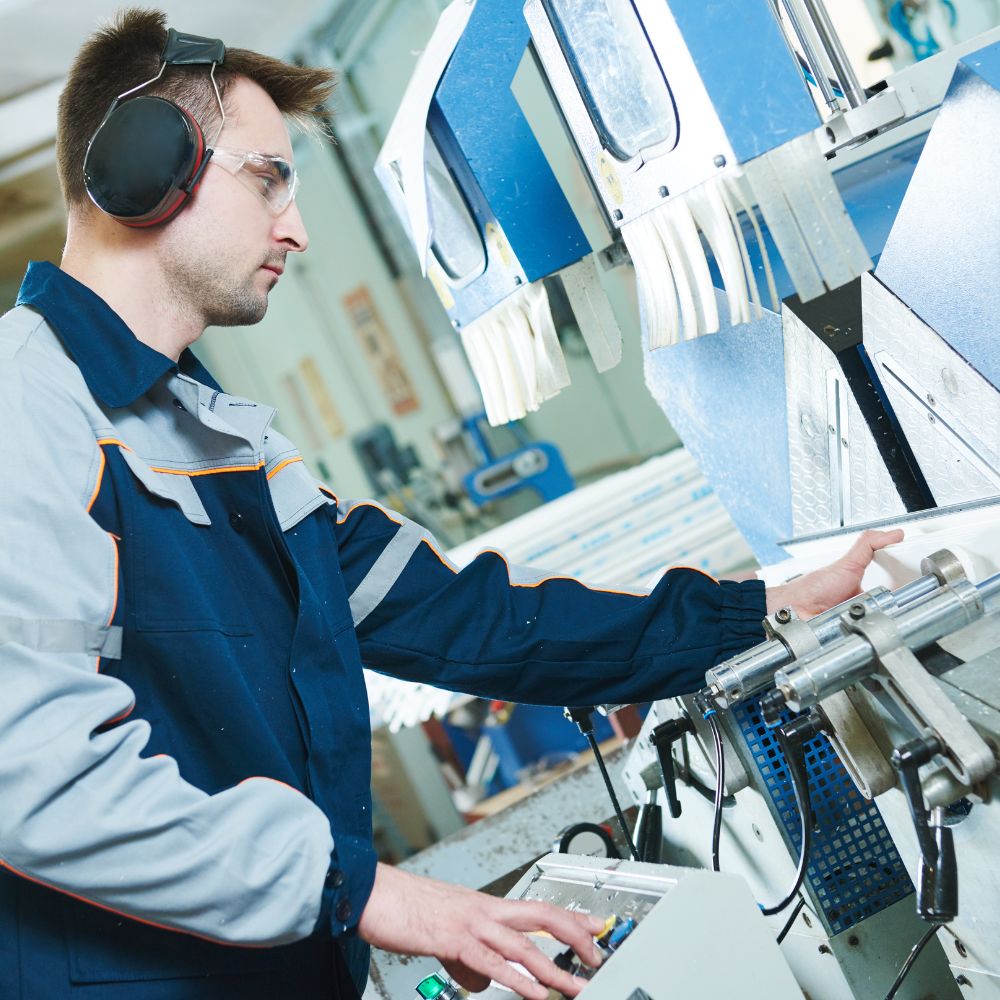

All formats of friction welding operate on the principle of heat-induced fusion between separate materials. Spin welding machines generate this friction by rotating one part into a fixed second part while applying pressure between both parts, creating localized heat at the contact point between the two materials.
Spin welding serves round (and non-round), balance-able parts that can be rotated at high RPM (often up to 16,000 RPM) about a common centerline. As lateral force is applied between the parts, the heated interface blends together, co-mingling the molecular structure of both pieces into one.
Once the joint is fused, force is removed, the now singular part is allowed to cool and the spin welding process is complete.
The machinery used to produce spin welds often looks like a lathe or drill press, the former rotating parts about a horizontal axis, and the latter about a vertical access. Aside from their orientation, spin welders typically come in one of two drive styles: inertia spin welders and continuous spin welders. Inertia welders rely on the kinetic energy of a flywheel to rotate parts together, whereas a continuous welder uses a coupled motor slowed by a mechanical brake.
Inertia welding is great for sensitive parts that can be damaged by applied rotational force during the welding process. Continuous welding is more advanced and offers complete rotational control throughout the welding cycle, but at a higher cost and with the complexity of the additional braking system.
In all cases, spin welding can be powered by electric (servo) or pneumatic motors.
Materials and Applications in Industrial Spin Welding
Spin Welding Applications
Spin welding applications are abundant, though not always so obvious to spot. Examples include:
Automating Industrial Spin Weld Fabrication
Semi-Automatic Spin Welding
Our AMS PJ-301 is a versatile, semi-standard system for spin welding, staking, textile welding, forming and spot welding. With semi-automatic operation, poka-yoke functions and outstanding productivity, the PJ-301 is an effective general-purpose plastic joining machine. This system is easily reconfigurable for future requirements.
High-Volume Spin Welding
Our AMS PJ-401 is designed for high-volume spin welding, ultrasonic plastic welding, staking and forming applications requiring precise joint profiles and specifications, exact locations, high levels of error-proofing and repeatability to ensure consistent joining. The PJ-401 offers larger part sizes, higher volumes, shorter cycle times, advanced recipe-driven PLC controls and extensive data reporting.